As businesses increasingly embrace cloud computing, the terminology surrounding various cloud models can be perplexing.
One of the fundamental distinctions lies in understanding the concept of a “public cloud” and how it differs from a “private cloud.”
According to internet firm CloudFlare, “A public cloud is a cloud service provided by a cloud provider to multiple customers. This model stands in contrast to the private cloud, and the services offered encompass Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). In a public cloud, services are accessed over the internet, and the underlying infrastructure is managed by the cloud provider.
Operating on remote servers, public cloud services are accessible to customers through the internet, offering flexibility and scalability for various organizational needs.
Understanding the key differences between public and private clouds is essential for businesses navigating the cloud landscape.
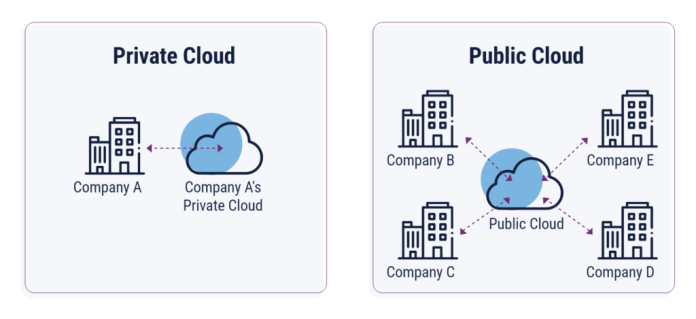
- Private Cloud: This is a cloud service exclusively dedicated to a single organization, ensuring that the cloud resources are not shared with any other entity. The user of a private cloud has exclusive access to the cloud environment.
- Public Cloud: In contrast, a public cloud shares computing resources among multiple customers. Although each customer’s data and applications remain concealed from others, the underlying infrastructure is communal.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations when deciding on their cloud strategy.
“While private clouds offer a more exclusive environment, they come with higher costs and potential resource inefficiencies. Public clouds, being more shared, are cost-effective and scalable but involve a trade-off in terms of privacy.”
This clarity becomes imperative as businesses evaluate their cloud needs, ensuring they align with the right model for their operations and data handling requirements.